COMPANY OVERVIEW.
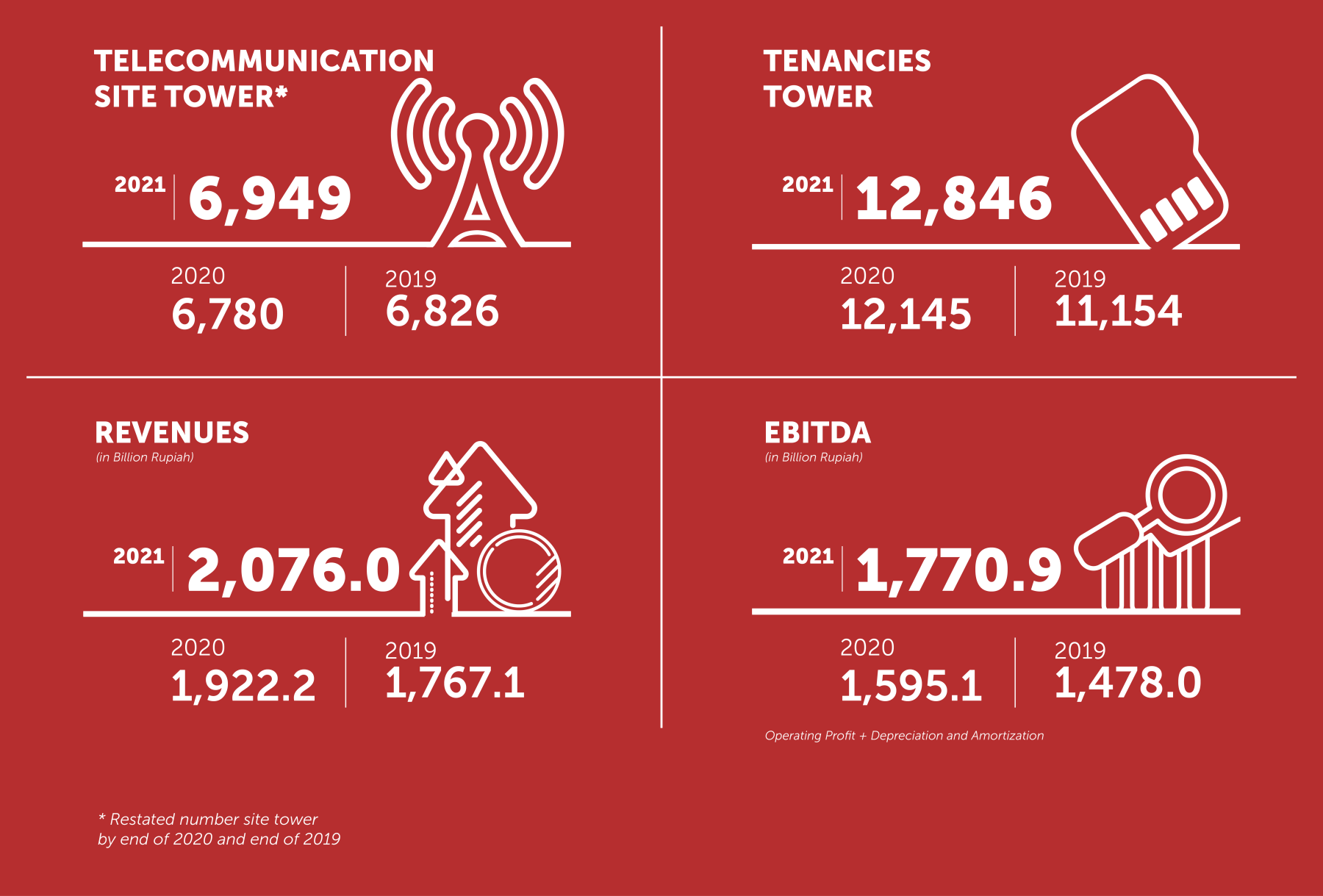
PT Solusi Tunas Pratama Tbk. (STP) was founded in 2006, and is now one of the leading independent tower companies in Indonesia. As of 31 December 2021, we owned and operated 6.949 tower with 12.846 tenancies, for a tenancy ratio of 1.85x. In October 2021, STP is officially acquired by PT Professional Telekomunikasi Indonesia (Protelindo) which is a subsidiary of PT Sarana Menara Nusantara Tbk.
GET TO KNOW US
.
TOWER OVERVIEW.
The Company operates telecommunications tower assets in all the 34 provinces in Indonesia, where 87% of the Company’s telecommunications tower sites are located in Java and Sumatra, two islands with the highest population density in Indonesia. As of 31 December 2020, the Company owned and operated 6,422 with 12,145 tenancies, for a tenancy ratio of 1.89x. In addition, the Company also has 38 indoor DAS networks and operates 3,000 km of fiber optic networks throughout Indonesia, including those through collaboration with PT Indonesia Comnets Plus.
TOWER CATEGORIES
STP has two tower categories, Greenfield Towers and Rooftop Towers. Greenfield Towers are standalone towers that require more space and are usually located in rural areas. Rooftop Towers are towers that are located on rooftops of buildings and are usually used in more urban areas.
Read More
TECHNOLOGY
At STP we believe in providing a better customer experience by maintaining and upgrading our technology continually. This is why we strive to always utilise the latest technology.
STP currently utilising microcell towers in Indonesia. A microcell is a cell in a mobile phone network served by a low power cellular base tower, usually covering a smaller or densely populated urban area such as a mall, a hotel, or a transportation hub. A microcell uses power control to limit the radius of its coverage area to less than two kilometres wide.
STP also utilises a Distributed Antenna System (DAS), which is a network of separated antenna nodes connected to a common source via a transport medium that provides wireless service within a geographic area or structure. The benefits of DAS is that less power is wasted in overcoming penetration and shadowing losses, and because a line-of-sight channel is present more frequently, leading to reduced fade depths and reduced delay spread.
STP IN NUMBERS.